Before you buy chocolate for your loved ones for Valentine’s Day, keep in mind that cacao percentage is one of the most important factors to consider when choosing chocolate. Here’s a quick guide so you can choose the right chocolate every time.
What is a cacao percentage?
It’s sometimes written as a simple percentage on the packaging, and other times you’ll see “% cacao” or “% cocoa”. Regardless of how they write it, they are all communicating the same information. The cacao percentage on the label or packaging indicates the ratio of cocoa to all other ingredients (such as sugar and milk powder). Cacao percentages range from 100% to less than 30%. When calculating the percentage, it’s important to know that the “cocoa” part of the equation includes cocoa beans and any cocoa products, such as cocoa mass, chocolate liquor, cocoa butter, and cocoa powder. The “other” ingredients can include fillers and flavorings like sugar, dairy, soy lecithin, vegetable oil, vanilla, etc. For example, a basic 70% Dark chocolate means that it is 70% cocoa and cocoa butter and 30% sugar.
Generally, the higher the percentage of cocoa in the chocolate, the more bitter it will taste. Unsweetened chocolate (which would be labeled as a 100% cocoa product) is used mostly for baking because it has no sugar added. However, there are a number of chocolate makers who produce 100% chocolate bars for eating out of hand. These bars are typically very intense. It’s important to note that not all chocolates with a higher cocoa percentage are unpleasant. Depending on the chocolate maker and the specific combination of chocolate liquor, cocoa butter, and cocoa powder they use in their recipe, the resulting chocolate can be downright luxurious.
Percentage of cocoa in the different types of chocolate
Each variety of chocolate has its own typical cocoa percentage depending on its type. Here is a quick overview of what proportions are used based on the different varieties of chocolate.
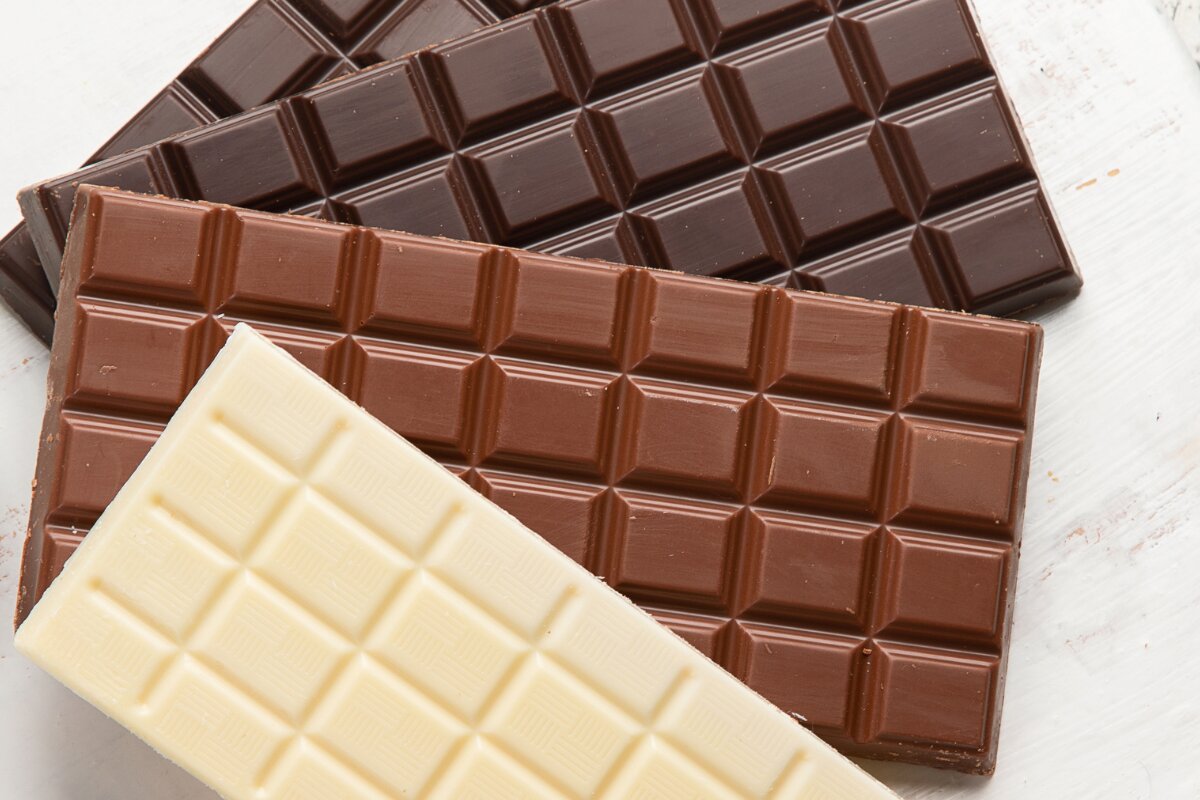
Dark chocolate
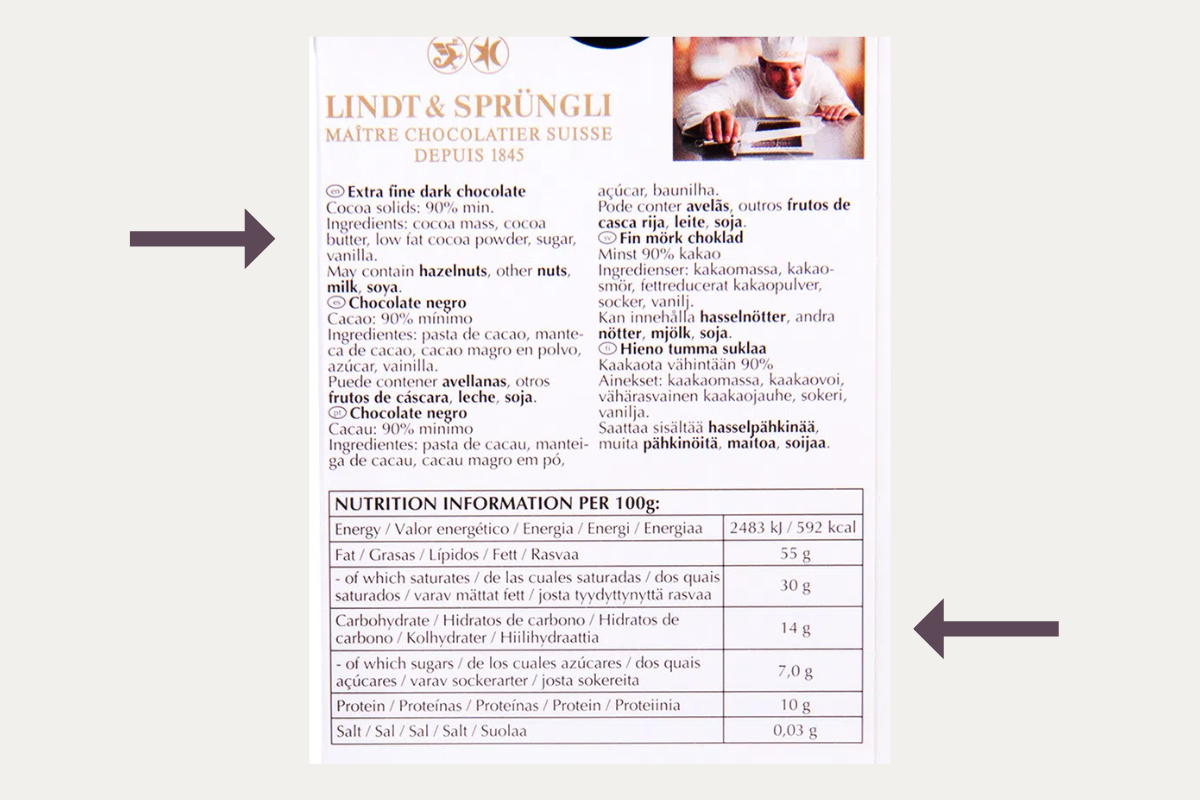
Dark chocolate is the chocolate with the most cocoa. It typically has at least 50% cocoa. The more cocoa the recipe contains, the darker and more intense it will be, which is why this chocolate is also known as “dark” chocolate, due to its color and powerful flavor. Each country can designate its own minimum percentages for it to be called “dark chocolate”. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), dark chocolate must contain at least 35% cocoa. Some dark chocolates have a very simple ingredient list with only two components, cocoa beans, and sugar. A basic 70% dark chocolate would be made from 70% cocoa beans and 30% sugar, and nothing else. If the ingredient list also includes cocoa butter, then the equivalent bar marked as a 70% dark chocolate would actually have less than 70% cocoa beans (the amount of cocoa butter is not typically disclosed separately but can be calculated from the nutritional details on the back label).
Milk chocolate
Unlike dark chocolate, milk chocolate is creamier in texture, more subtle in flavor, and lighter in color. Its sweet flavor is achieved thanks to the mixture of chocolate with powdered milk and sugar to reduce the intensity of the cocoa flavor and make it more palatable for the mass market.
The most common ratio is 40% cocoa, although there are also “dark milk” bars that use 50% cocoa or more. Remember that the percentage is a combination of cocoa beans plus added cocoa butter (which is simply the fat from the cocoa beans and doesn’t contribute to the overall chocolate flavor), so 40% milk chocolate might be 20% cocoa beans and 20% cocoa butter. This is quite different from 70% dark chocolate which might be made of 70% cocoa beans. One benefit of adding milk to chocolate is that it gives the chocolate more nutritional value due to the calcium content, although the amount of sugar also tends to be higher.
White chocolate
White chocolate doesn’t typically provide cocoa % on the label. Many do not consider white chocolate to be “real” chocolate since it has only 20%-30% cocoa butter, with the rest being milk solids, sugar, vegetable fat, sweeteners, milk fat, and other ingredients. Note that there are no cocoa beans in white chocolate, so why wouldn’t the percentage always be 0%? As mentioned previously, the cocoa % is calculated as the sum of all cocoa products including cocoa butter. For some chocolate eaters, this makes for a lower-quality of chocolate.
Also, white chocolate is not recommended for frequent consumption because its fat and sugar content is very high compared to other types of chocolate.
How can I find out the cocoa percentage in my chocolate?
Most chocolates have the percentage of cocoa printed on the front label or packaging. Brands often brag about the high percentage of cocoa found in their products, such as 70%, 80%, and 90%, so it’s often not hard to find. For some reason, if you can’t find the information on the label, you can usually find it in the ingredient list.
Is cocoa percentage an indicator of quality?
Many people believe that the higher the percentage of cocoa in dark chocolate, the better the chocolate quality. However, this is not necessarily true. A higher cocoa content does not necessarily mean that the quality of the chocolate is also higher. Let’s take wine as an example: it’s not the % alcohol content that determines the quality but rather the terroir (origin, climate, plantation) and post-harvest treatment (fermentation). The same is true with chocolate: it’s not the % cocoa but the quality of beans that makes the chocolate stand out. It’s a combination of cacao variety, the terroir (origin and climate), and post-harvest treatment (fermentation and roasting) that impacts the quality the most.
Now that you know the importance of choosing the right chocolate and its associated cocoa percentage, make sure that you also consider where the beans come from. West African cacao tends to be used for mass-market chocolate products. There are some really delicious flavors coming out of Central and South America, with smaller farms in Vietnam and India also producing quality beans. Organic cacao will be healthier too, and free from pesticides. You can also look for chocolate bars that carry the fair trade certification logo; this indicates that labor practices are ethical and that farmers are being paid fair prices.
In addition to the beans and their origin, the production process also matters. Basic ingredients, careful roasting, and skilled blending of the beans and flavorings will result in a more delicious and nutritious product. You are more likely to find what you want when buying chocolate from smaller-scale producers, not giant candy corporations.
If you have any questions or comments, we would love to hear from you! We are @cocoterra_co on Instagram and Pinterest and @cocoterraco on Twitter and Facebook. Don’t forget to tag us when you show off your creations.








